

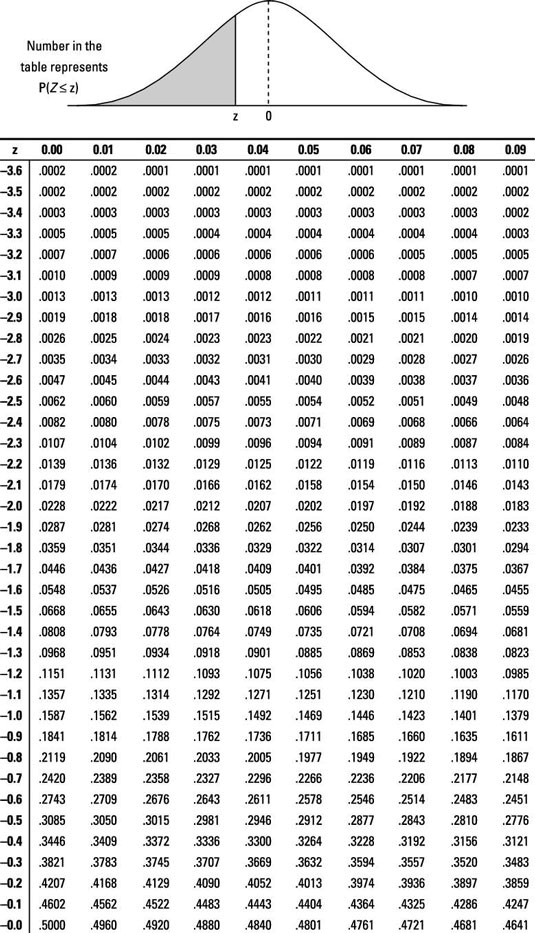
Statistic of 0.5 based on a sample size of 400. 025.Īnother Example: Suppose a company states that they receive 200 orders a day but you believe this number is not correct (Ha: μ ≠ 200). However, since this is right-tail hypothesis testing, to calculate the actual p-value, we must take 1 and The sample size is 10, so we are going to look up the p-value based on the T-distribution table. So this is right-tail hypothesis testing. Let's say you locate 10 customers (n=10) to find out their experience and obtain a test statistic of 1.96. You believe that the average is much less than this (Ha: μ 4). Suppose that a company claims that the null hypothesis that the average dollar amount that customers spend per transaction is $32 (H0: μ = 32). Let's go through a few examples on calculating the p-value. So the significance level represents the cut-off point that we choose and determines with what level of confidence we can accept results. If the significance level is 10% and the p-value is lower than this amount, this means that we can accept the null hypothesis with If the significance level is 0.1% and the p-value is lower than this amount, this means that we can accept the null hypothesis withĩ9.9% confidence. If the significance level is 1% and the p-value is lower than this 1%, this means that we can accept the null hypothesis This means that if the p-value is lower than the 5% significance level, this means that we can accept the The most commonly used significance level is probably 5%. The higher the significance level, the larger the range we have for accepting the null hypothesis. The narrower the range we have for accepting the null hypothesis. The significance level, α, is the value that we set as the cutoff point for whether we reject a null hypothesis or not. This accounts for both the left-tail (less than)Īnd the right-tail (greater than) possibilities. If the testing type is two-tail, then we need to double the p-value obtained from the test statistic. If the testing type is right-tail instead of left-tail, then the p-value is, 1- p-value.
The hypothesis testing type gives us a frame of reference. This can be left-tail (Ha: μ H0), or two-tail (Ha: μ ≠ H0) testing. Next, we must know the hypothesis testing type. It determines whether we need to use the t-distribution or the Z-distribution This is why the sample size is very important. When the sample size is large, we use the Z-distribution to calculate the If the sample size is less than 30 (n30), we consider this a large sample size. Standard normal distribution (Z-distribution) to look up the p-value or we use the t-distribution to look up the p-value. The sample size is very important because it determines whether we use the The sample size is another variable we need to calculate the p-value. So the test statistic is very important because it gives us a standardized measure that shows how far or close actual results are from claimed data. The distance is larger, the actual data shows that we should reject the null hypothesis (H 0). If the distance between the claimed value and theĪctual obtained results is small in terms of standard errors, the data is not far from the claim and the chances are the claimed hypothesis (data) is true. Measure that tells us how far the actual data results obtained are from the claimed data (from the null hypothesis). The test statistic represents the distance between the actual sample results and the claimed value in terms of standard errors. This is where the test statistic plays an important role. You have to extract meaningful things from it. You can obtain a whole bunch of data points for a given scenario, but When you're working with data, the numbers of the data itself is not very meaningful,īecause it's not standardized. Hypothesis testing type (left tail, right tail, or two-tail), and the significance level (α). To calculate the p-value, this calculator needs 4 pieces of data: the test statistic, the sample size, the If the p-value is greater than or equal to α, we cannot reject the claimed hypothesis. That we can reject the claimed hypothesis. If the p-value is less than α, then this represents a statistically significant p-value. This cutoff point is also called the alpha level (α). We set the significance level, which serves as the cutoff level, for whether a The p-value is a quantitative value that allows us to determine whether a null hypothesis (or claimed hypothesis) is true.ĭetermining the p-value allows us to determine whether we should reject or not reject a


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
